Efectos de emulsiones lipídicas intravenosas sobre irisin, MMP-9, NF-κB, TNF-α en riñones de ratas con toxicidad por bupivacaína: estudio inmunohistoquímico
Resumen
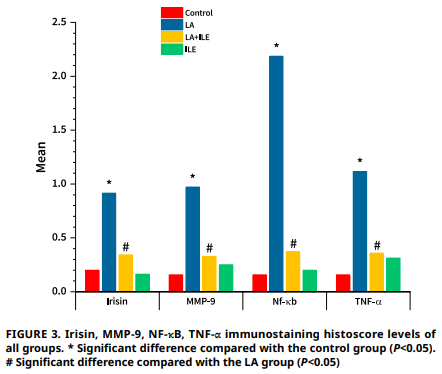
Este estudio investigó los efectos de la toxicidad inducida por bupivacaína en el tejido renal y el posible papel protector de la emulsión lipídica intravenosa. Veintiocho ratas Wistar Albino macho adultas fueron asignadas aleatoriamente a cuatro grupos: Control, anestesia local, emulsión lipídica intravenosa y anestesia local + emulsión lipídica intravenosa. El grupo anestesia local recibió una infusión de bupivacaína de 3 μg·kg-1·min-1, el grupo emulsión lipídica intravenosa recibió un bolo de 1,5 mL seguido de una infusión de emulsión lipídica intravenosa de 0,25 μg·kg-1·min-1, y el grupo anestesia local + emulsión lipídica intravenosa recibió bupivacaína con intervención de emulsión lipídica intravenosa al observar signos de toxicidad. Todos los animales fueron monitoreados de cerca durante el estudio. En el grupo anestesia local, la bupivacaína indujo alteraciones renales significativas, incluyendo un aumento en la inmunorreactividad de irisina, metaloproteinasa de matriz-9, factor nuclear kappa B y factor de necrosis tumoral-α en comparación con los controles (P<0,05). La histopatología reveló edema, congestión, degeneración tubular, infiltración, degeneración glomerular y desprendimiento de células tubulares significativos (P<0,001). Por el contrario, las ratas del grupo anestesia local + emulsión lipídica intravenosa mostraron disminución del edema y congestión renal, atenuación de la degeneración tubular y reducción de la infiltración, degeneración glomerular y desprendimiento celular tubular (P<0,001), indicando un efecto nefroprotector de emulsión lipídica intravenosa. Estos hallazgos sugieren que irisina, factor nuclear kappa B, metaloproteinasa de matriz-9 y factor de necrosis tumoral-α son biomarcadores fiables de la nefrotoxicidad inducida por bupivacaína. La administración de emulsión lipídica intravenosa atenúa estos cambios bioquímicos e histopatológicos, destacando su potencial como agente protector frente al daño renal inducido por anestésicos locales. El estudio subraya la importancia de monitorear estos biomarcadores y proporciona evidencia de los beneficios terapéuticos de emulsión lipídica intravenosa en el manejo de la toxicidad por bupivacaína.
Descargas
Citas
Yılmaz N. Double complication developed in a patient related to local anesthetics. Turkiye Klinikleri J. Case Rep. [Internet]. 2022; 30(1):37–39. doi: https://doi.org/qqk3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.5336/caserep.2021-85435
Long B, Chavez S, Gottlieb M, Montrief T, Brady WJ. Local anesthetic systemic toxicity: A narrative review for emergency clinicians. Am. J. Emerg. Med. [Internet]. 2022; 59:42–48. doi: https://doi.org/gskgtm DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2022.06.017
Dickerson DM, Apfelbaum JL. Local anesthetic systemic toxicity. Aesthet. Surg. J. [Internet]. 2014; 34(7):1111–1119. doi: https://doi.org/gr9hgh DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1090820X14543102
Malafi ME, Desai D. Serious side effects of local anesthetics’s absorption in blood stream. J. Anesth. Pain Med. [Internet]. 2023; 8(3):152–153. doi: https://doi.org/qqk4 DOI: https://doi.org/10.33140/JAPM.08.03.05
Lee HT, Krichevsky IE, Xu H, Ota-Setlik A, D’Agati VD, Emala CW. Local anesthetics worsen renal function after ischemia- reperfusion injury in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. [Internet]. 2004; 286(1):F111-F119. doi: https://doi.org/cj3tjs DOI: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00108.2003
Qiao X, Bhave S, Swain L, Zweck E, Reyelt L, Crowley P, Annamalai SK, Chennjorwala A, Esposito M, Razavi A, Foroutanjazi S, Machen C, Thayer K, Jorde L, Karas RH, Kapur NK. Myocardial injury promotes matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity in the renal cortex in preclinical models of acute myocardial infarction. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. [Internet]. 2022; 15(2):207–216. doi: https://doi.org/qqk5 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-021-10114-y
Song N, Xu Y, Paust HJ, Panzer U, de Las Noriega MM, Guo L, Renné T, Huang J, Meng X, Zhao M, Thaiss F. IKK1 aggravates ischemia-reperfusion kidney injury by promoting the differentiation of effector T cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. [Internet]. 2023; 80(5):125. doi: https://doi.org/qqk6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-023-04763-2
Yang H, Xie T, Li D, Du X, Wang T, Li C, Song X, Xu L, Yi F, Liang X, Gao L, Yang X, Ma C. Tim-3 aggravates podocyte injury in diabetic nephropathy by promoting macrophage activation via the NF-κB /TNF-α pathway. Mol. Metab. [Internet]. 2019; 23:24–36. doi: https://doi.org/gmbzzk DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2019.02.007
Zhang N, Guan C, Liu Z, Li C, Yang C, Xu L, Niu M, Zhao L, Zhou B, Che L, Wang Y, Xu Y. Calycosin attenuates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury by suppressing NF-κB mediated inflammation via PPARγ/EGR1 pathway. Front. Pharmacol. [Internet]. 2022; 13:970616. doi: https://doi.org/qqk7 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.970616
Jin YH, Li ZY, Jiang XQ, Wu F, Li ZT, Chen H, Xi D, Zhang YY, Chen ZQ. Irisin alleviates renal injury caused by sepsis via the NF-κB signaling pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. [Internet]. 2020; 24(11):6470–6476. doi: https://doi.org/gt3jd2
Cohen M, Meisser A, Haenggeli L, Bischof P. Involvement of MAPK pathway in TNF – alpha-induced MMP-9 expression in human trophoblastic cells. Mol. Hum. Reprod. [Internet]. 2006; 12(4):225–232. doi: https://doi.org/ds9wcz DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/molehr/gal023
Qiongyue Z, Xin Y, Meng P, Sulin M, Yanlin W, Xinyi L, Xuemin S. Post-treatment with irisin attenuates acute kidney injury in sepsis mice through anti-ferroptosis via the SIRT1/Nrf2 pathway. Front. Pharmacol. [Internet]. 2022; 13:857067. doi: https://doi.org/grt46r DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.857067
Fettiplace MR, Weinberg G. Past, present, and future of lipid resuscitation therapy. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. [Internet]. 2015; 39(1S):72S-83S. doi: https://doi.org/f7nxmt DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0148607115595979
Neal JM, Neal EJ, Weinberg GL. American society of regional anesthesia and pain medicine local anesthetic systemic toxicity checklist: 2020 version. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. [Internet]. 2021; 46(1):81–82. doi: https://doi.org/gr9hf6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1136/rapm-2020-101986
Wu G, Sun B, Liu LI, Zhou J, Mo L, Ren C, Ou C: Lipid emulsion mitigates local anesthesia-induced central nervous system toxicity in rats. Exp. Ther. Med. [Internet]. 2015; 10(3):1133– 1138. doi: https://doi.org/qqk8 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2015.2594
Harvey M, Cave G. Lipid emulsion in local anesthetic toxicity. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. [Internet]. 2017; 30(5):632–638. doi: https://doi.org/qqk9 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/ACO.0000000000000498
Chen Y, Xia Y, Liu L, Shi T, Shi K, Wang Q, Chen L, Papadimos TJ, Xu X. Lipid emulsion reverses bupivacaine-induced asystole in isolated rat hearts: concentration – response and time- response relationships. Anesthesiology [Internet]. 2010; 113(6):1320–1325. doi: https://doi.org/b6w3ph DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181fc63ed
Gheisari R, Saatchi M, Estakhri F, Vossoughi M, Bazaei M, TGF-β1/periostin•MMP-2 signaling pathway. PLoS One Khosravani Z. Effect of local anesthetics on renal function: An animal study in Iran. Dent Res J (Isfahan). [Internet]. 2023; 26(20):106. doi: https://doi.org/qqmb DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/drj.drj_200_23
Yılmaz N, Doğukan M, Türk A, Tosun F. Cardioprotective effect of intravenous lipid emulsion in bupivacaine-induced experimental cardiac toxicity. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. [Internet]. 2023; 29(6):683–688. doi: https://doi.org/qqmc DOI: https://doi.org/10.9775/kvfd.2023.30177
Edwards J, Kowal M, VanDreel A, Lamar P, Prozialeck W. A method for the evaluation of site-specific nephrotoxic injury in the intact rat kidney. Toxics [Internet]. 2020; 8(1):4. doi: https://doi.org/gv595c DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics8010004
Eser N, Yoldas A, Turk A, Kalaycı-Yigin A, Yalcin A, Cicek M. Ameliorative effects of garlic oil on FNDC5 and irisin sensitivity in liver of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. [Internet]. 2021; 73(6):824–834. doi: https://doi.org/pqjt DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/jpp/rgab023
Hsu SM, Raine L, Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J. Histochem. Cytochem. [Internet]. 1981; 29(4):577–580. doi: https://doi.org/b573dv DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/29.4.6166661
Kaplan S, Türk A, Aydın H, Erten M, Kırıcı P. Vitamin D improves oxidative stress and histopathological damage in rat ovaries caused by hyperthyroidism. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. [Internet]. 2021; 47(10):3551–3560. doi: https://doi.org/qqmd DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jog.14948
Chen L, Zhuang K. Kaempferol counteracts bupivacaine-induced neurotoxicity in mouse dorsal root ganglia neurons by regulating TRAF6-dependent NF-κB signaling. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. [Internet]. 2023; 39(7):710–717. doi: https://doi.org/qqmf DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/kjm2.12682
Boström P, Wu J, Jedrychowski MP, Korde A, Ye L, Lo JC, Rasbach KA, Boström EA, Choi JH, Long JZ, Kajimura S, Zingaretti MC, Vind BF, Tu H, Cinti S, Højlund K, Gygi SP, Spiegelman BM. A PGC1-α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature [Internet]. 2012; 481(7382): 463–468. doi: https://doi.org/fz2h25 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10777
Aydin S, Kuloglu T, Aydin S, Eren MN, Celik A, Yilmaz M, Kalayci M, Sahin İ, Gungor O, Gurel A, Ogeturk M, Dabak O. Cardiac, skeletal muscle and serum irisin responses to with or without water exercise in young and old male rats: cardiac muscle produces more irisin than skeletal muscle. Peptides [Internet]. 2014; 52:68–73. doi: https://doi.org/gkgpzm DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2013.11.024
Li X, Lindholm B. The role of irisin in kidney diseases. Clin. Chim. Acta [Internet]. 2024; 554:117756. doi: https://doi.org/gtm56h DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2023.117756
Zhu D, Wang H, Zhang J, Zhang X, Xin C, Zhang F, Lee Y, Zhang L, Lian K, Yan W, Ma X, Liu Y, Tao L. Irisin improves endothelial function in type 2 diabetes through reducing oxidative/nitrative stresses. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. [Internet]. 2015; 87:138–147. doi: https://doi.org/f7zsvw DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2015.07.015
Wang Y, Deng X, Wei J, Yang Z, Du Y, Song S, Shi Y, Wu H: Irisin ameliorates UUO – induced renal interstitial fibrosis through [Internet]. 2024; 19(6): e0299389. doi: https://doi.org/qqmg DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0299389
Peng H, Wang Q, Lou T, Qin J, Jung S, Shetty V, Li F, Wang Y, Feng XH, Mitch WE, Graham BH, Hu Z. Myokine mediated muscle- kidney crosstalk suppresses metabolic reprogramming and fibrosis in damaged kidneys. Nat. Commun. [Internet]. 2017; 8(1):1493. doi: https://doi.org/gckzzs DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-01646-6
Liu Y, Fu Y, Liu Z, Shu S, Wang Y, Cai J, Tang C, Dong Z. Irisin is induced in renal ischemia-reperfusion to protect against tubular cell injury via suppressing p53. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. [Internet]. 2020; 1866(7):165792. doi: https://doi.org/gt7nkk DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165792
Yabluchanskiy A, Ma Y, Iyer RP, Hall ME, Lindsey ML. Matrix metalloproteinase-9: Many shades of function in cardiovascular disease. Physiology [Internet]. 2013; 28(6):391–403. doi: https://doi.org/f5gjr9 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1152/physiol.00029.2013
Wang Y, Jiao L, Qiang C, Chen C, Shen Z, Ding F, Lv L, Zhu T, Lu Y, Cui X. The role of matrix metalloproteinase 9 in fibrosis diseases and its molecular mechanisms. Biomed. Pharmacother. [Internet]. 2024; 171:116116. doi: https://doi.org/g9kpjp DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2023.116116
Pang G, Ye L, Jiang Y, Wu Y, Zhang R, Yang H, Yang Y. Unveiling the bidirectional role of MMP9: A key player in kidney injury. Cell. Signal. [Internet]. 2024; 122:111312. doi: https://doi. org/qqmh DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111312
Lelongt B, Bengatta S, Delauche M, Lund LR, Werb Z, Ronco PM. Matrix metalloproteinase 9 protects mice from anti- glomerular basement membrane nephritis through its fibrinolytic activity. J. Exp. Med. [Internet]. 2001; 193(7):793– 802. doi: https://doi.org/db6q9z DOI: https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.193.7.793
Bengatta S, Arnould C, Letavernier E, Monge M, de Préneuf HM, Werb Z, Ronco P, Lelongt B. MMP9 and SCF protect from apoptosis in acute kidney injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. [Internet]. 2009; 20(4):787–797. doi: https://doi.org/ftksf7 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2008050515
Wang X, Zhou Y, Tan R, Xiong M, He W, Fang L, Wen P, Jiang L, Yang J. Mice lacking the matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene reduce renal interstitial fibrosis in obstructive nephropathy. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. [Internet]. 2010; 299(5):F973-F982. doi: https://doi.org/b7c2t2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00216.2010
Io H, Hamada C, Ro Y, Ito Y, Hirahara I, Tomino Y. Morphologic changes of peritoneum and expression of VEGF in encapsulated peritoneal sclerosis rat models. Kidney Int. [Internet]. 2004; 65(5):1927–1936. doi: https://doi.org/bs22bp DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.00599.x
Zou G, Zhou Z, Xi X, Huang R, Hu H. Pioglitazone Ameliorates Renal Ischemia – Reperfusion Injury via Inhibition of NF-κB Activation and Inflammation in Rats. Front. Physiol. [Internet]. 2021; 12:707344. doi: https://doi.org/qqmj DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2021.707344
Zhang Y, Hu F, Wen J, Wei X, Zeng Y, Sun Y, Luo S, Sun L. Effects of sevoflurane on NF-кB and TNF-α expression in renal ischemia-reperfusion diabetic rats. Inflamm. Res. [Internet]. 2017; 66(10):901–910. doi: https://doi.org/gbw4gb DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-017-1071-1
Tan RZ, Li JC, Zhu BW, Huang XR, Wang HL, Jia J, Zhong X, Liu J, Wang L, Lan HY. Neuropeptide Y protects kidney from acute kidney injury by inactivating M1 macrophages via the Y1R – NF-κB – Mincle-dependent mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Sci. [Internet]. 2023; 19(2):521–536. doi: https://doi.org/gtbnmp DOI: https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.80200
Hu Z, Chen D, Yan P, Zheng F, Zhu H, Yuan Z, Yang X, Zuo Y, Chen C, Lu H, Wu L, Lyu J, Bai Y. Puerarin suppresses macrophage M1 polarization to alleviate renal inflammatory injury through antagonizing TLR4/MyD88-mediated NF-κB p65 and JNK/FoxO1 activation. Phytomedicine [Internet]. 2024; 132:155813. doi: https://doi.org/hbf7qt DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155813
Jiao H, Zhang M, Xu W, Pan T, Luan J, Zhao Y, Zhang Z. Chlorogenic acid alleviate kidney fibrosis through regulating TLR4/NF-қB mediated oxidative stress and inflammation. J. Ethnopharmacol. [Internet]. 2024; 335:118693. doi: https://doi.org/g9rtjm DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2024.118693
Zhang L, Wang J, Xu T, Luo Y, Cai Z, Jiang Y, Jin T, Bao H, Wang Y. Bicyclol alleviates obesity-induced renal injury by inhibiting JNK and NF-κB – mediated inflammation. Int. Immunopharmacol. [Internet]. 2024; 129:111609. doi: https://doi.org/qqmk DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111609
Zhao G, Lu S, Li L, Fan X. Local anesthetic articaine ameliorates LPS-induced acute kidney injury via inhibition of NF-ĸB activation and the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. [Internet]. 2020; 34(10):e22554. doi: https://doi.org/qqmm DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.22554
Song M, Chen Y. Local anaesthetic procaine derivatives protect rat against diabetic nephropathy via inhibition of DPP-4, inflammation and oxidative stress. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. [Internet]. 2023; 102(1):26–37. doi: https://doi.org/qqmp DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/cbdd.14252
Karnina R, Arif SK, Hatta M, Bukhari A, Natzir R, Hisbullah, Patellongi I, Kaelan C. Systemic lidocaine administration influences NF-kβ gene expression, NF-kβ and TNF – α protein levels on BALB/c mice with musculoskeletal injury. Ann. Med. Surg. [Internet]. 2021; 69:102660. doi: https://doi.org/g7kfw3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amsu.2021.102660
Piegeler T, Votta-Velis EG, Bakhshi FR, Mao M, Carnegie G, Bonini MG, Schwartz DE, Borgeat A, Beck-Schimmer B, Minshall RD. Endothelial barrier protection by local anesthetics: ropivacaine and lidocaine block tumor necrosis factor-α-induced endothelial cell Src activation. Anesthesiology [Internet]. 2014; 120(6):1414–1428. doi: https://doi.org/f572fc DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0000000000000174
Fu Z, Ye Q, Zhang Y, Zhong Z, Xiong Y, Wang Y, Hu L, Wang W, Huang W, Shiu-Chung Ko D. Hypothermic machine perfusion reduced inflammatory reaction by downregulating the expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 in a reperfusion model of donation after cardiac death. Artif. Organs. [Internet]. 2016; 40(6):E102-E111. doi: https://doi.org/f8sx2f DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/aor.12658
Nee LE, McMorrow T, Campbell E, Slattery C, Ryan MP. TNF-alpha and IL-1beta – mediated regulation of MMP-9 and TIMP-1 in renal proximal tubular cells. Kidney Int. [Internet]. 2004; 66(4):1376–1386. doi: https://doi.org/dkmndd DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.00900.x
Seong-Ho O, Jeong-Min H, Soo HL, Ju-Tae S. Lipid emulsion for treating local anesthetic systemic toxicity. Int. J. Med. Sci. [Internet]. 2018; 15(7):713–722. doi: https://doi.org/gqpmnc DOI: https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.22643
Weinberg GL, Ripper R, Murphy P, Edelman LB, Hoffman W, Strichartz G, Feinstein DL. Lipid infusion accelerates removal of bupivacaine and recovery from bupivacaine toxicity in the isolated rat heart. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. [Internet]. 2006; 31(4):296–303. doi: https://doi.org/bhrvd3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rapm.2005.02.011
Shi K, Xia Y, Wang Q, Wu Y, Dong X, Chen C, Tang W, Zhang Y, Luo M, Wang X, Papadimos TJ, Xu X. The effect of lipid emulsion on pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of bupivacaine in rats. Anesth. Analg. [Internet]. 2013; 116(4):804–809. doi: https://doi.org/qqmq DOI: https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0b013e318284123e