Application of Deep Learning for the rapid and accurate diagnostic of bone fractures in dogs using radiographic images
Abstract
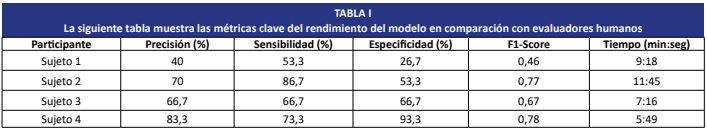
Radiography remains the most widely used diagnostic tool in veterinary medicine for detecting bone fractures in dogs. However, manual interpretation can be affected by the clinician’s level of experience, as well as by factors such as fatigue or excessive workload. In this context, the present study evaluated the performance of a deep learning model based on the YOLOv5 architecture, aimed at diagnostic canine radiographic images divided into two categories: presence or absence of fracture. The model achieved an accuracy of 83.3%, significantly outperforming three general practice veterinarians, whose accuracy ranged from 40% to 70%. Furthermore, the automated system reduced the average diagnostic time by 40%, delivering classifications within seconds. These results highlight the feasibility of artificial intelligence as a tool to enhance diagnostic precision, speed, and consistency in veterinary medicine, especially in resource- constrained environments. Further dataset expansion and clinical validation are recommended.
Downloads
References
Couch JR. Artificial Intelligence: Past, Present and Future. J. SC Acad. Sci. [Internet]. 2023 [citado 08 Enero 2025]; 21(1):2. Disponible en: https://goo.su/SYEdM
Anwar SM, Majid M, Qayyum A, Awais M, Alnowami M, Khan MK. Medical Image Analysis using Convolutional Neural Networks: A Review. J. Med. Syst. [Internet]. 2018; 42(11):226. doi: https://doi.org/gfghhd DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-018-1088-1
Appleby RB, Basran PS. Artificial intelligence in veterinary medicine. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. [Internet]. 2022; 260(8):819–824. doi: https://doi.org/p7f6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.2460/javma.22.03.0093
Davenport T, Kalakota R. The potential for artificial intelligence in healthcare. Future Healthc. J. 2019; 6(2):94–98. doi: https://doi.org/ggf26q DOI: https://doi.org/10.7861/futurehosp.6-2-94
Rajpurkar P, Irvin J, Zhu K, Yang B, Mehta H, Duan T, Ding D, Bagul A, Langlotz C, Shpanskaya K, Lungren MP, Ng AY. CheXNet: Radiologist-Level Pneumonia Detection on Chest X-Rays with Deep Learning. Cornell University: Arxiv; 2018 [citado 08 Enero 2025]. doi: https://doi.org/g88dtm
Lubinus Badillo F, Rueda Hernández CA, Marconi Narváez B, Arias Trillos YE. Redes neuronales convolucionales: un modelo de Deep Learning en imágenes diagnósticas. Revisión de tema. Rev. Colomb. Radiol. 2021; 32(3):5591– 5599. doi: https://doi.org/p7f7 DOI: https://doi.org/10.53903/01212095.161
Mora-Tola MA, Carpio-Alemán FM, Mora-Tola JD, Román-Cárdenas FA. Characterization of fractures of the appendicular skeleton in dogs according to the AO classification. Polo Conoc. 2023 [citado 08 Enero 2025]; 8(3):2440–2457. Disponible en: https://goo.su/4fgGIK6
DeCamp CE, Johnston SA, Dejardin LM, Schaefer SL. Brinker, Piermattei and Flo’s Handbook of Small Animal Orthopedics and Fracture Repair. 5th ed. St. Louis: Saunders; 2016.
McEvoy FJ, Amigo JM. Using machine learning to classify image features from canine pelvic radiographs: evaluation of partial least squares discriminant analysis and artificial neural network models. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound. 2013; 54(2):122–126. doi: https://doi.org/f4rr93 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/vru.12003
Shen D, Wu G, Suk HI. Deep learning in medical image analysis. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2017; 19(1):221–248. doi: https://doi.org/gcgmb4 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-bioeng-071516-044442
Rajpurkar P, Irvin J, Ball RL, Zhu K, Yang B, Mehta H, Duan T, Ding D, Bagul A, Langlotz CP, Patel BN, Yeom KW, Shpanskaya K, Blankenberg FG, Seekins J, Amrhein TJ, Mong DA, Halabi SS, Zucker EJ, Ng AY, Lungren MP. Deep learning for chest radiograph diagnosis: a retrospective comparison of the CheXNeXt algorithm to practicing radiologists. PLoS Med. 2018; 15(11):e1002686. doi: https://doi.org/gfnkcv DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002686
Taha AA, Hanbury A. Metrics for evaluating 3D medical image segmentation: analysis, selection, and tool. BMC Med. Imaging. 2015; 15(1):29. doi: https://doi.org/gb343z DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12880-015-0068-x
Lakhani P, Sundaram B. Deep learning at chest radiography: automated classification of pulmonary tuberculosis by using convolutional neural networks. Radiology. 2017; 284(2):574–582. doi: https://doi.org/gbp274 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2017162326
Schmidhuber J. Deep learning in neural networks: an overview. Neural Netw. 2015; 61:85–117. doi: https://doi.org/f6v78n DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2014.09.003
Nature Machine Intelligence. A prize for discoveries past, present and future. Nat. Mach. Intell. [Internet]. 2019; 1(5):201. doi: https://doi.org/p7hf DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42256-019-0054-z
Netter A, Noorzadeh S, Duchateau F, Abrao H, Desternes J, Peyras J, et al. Initial Results in the Automatic Visual Recognition of Endometriosis Lesions by Artificial Intelligence During Laparoscopy: A Proof-of-Concept Study. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2025 Sep 3. Online. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmig.2025.08.027 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmig.2025.08.027
Kukartsev VV, Ageev RA, Borodulin AS, Gantimurov AP, Kleshko II. Deep learning for object detection in images: development and evaluation of the YOLOv8 model using Ultralytics and Roboflow libraries. In: Silhavy R, Silhavy P, editors. Software Engineering Methods Design and Application. CSOC 2024. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems. Cham: Springer; 2024. p. 630. doi: https://doi.org/p7hg DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-70285-3_48
Gulshan V, Peng L, Coram M, Stumpe MC, Wu D, Narayanaswamy A, Venugopalan S, Widner K, Madams T, Cuadros J, Kim R, Raman R, C. Nelson P, Mega JL, Webster DR. Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm for detection of diabetic retinopathy in retinal fundus photographs. JAMA. 2016; 316(22):2402-2410. doi: https://doi.org/gcgk7d DOI: https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.17216
Guarnido-Lopez P, Ramirez-Agudelo JF, Denimal E, Benaouda M. Programming and setting up the object detection algorithm YOLO to determine feeding activities of beef cattle: A comparison between YOLOv8m and YOLOv10m. Animals. 2024; 14(19):2821. doi: https://doi.org/p7hh DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14192821
Abeliuk A, Gutiérrez C. Historia y evolución de la inteligencia artificial. Rev. Bits Cienc. 2021; 21:14-21. doi: https://doi.org/p7hj
Bengio Y, LeCun Y, Hinton G. Deep learning for AI. Commun ACM. 2021; 64(7):58–65. doi: https://doi.org/gkx7tb DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/3448250
Esteva A, Kuprel B, Novoa RA, Ko J, Swetter SM, Blau HM, Thrun S. Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature. 2017; 542(7639):115–118. doi: https://doi.org/bxwn DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21056
Gerke S, Minssen T, Cohen G. Ethical and legal challenges of artificial intelligence-driven healthcare. In: Bohr A, Memarzadeh K, editors. Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare. Amsterdam: Academic press; 2020. p. 295–336. doi: https://doi.org/gxww DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-818438-7.00012-5
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR); Las Vegas, NV, USA; 2016. p. 770–778. doi: https://doi.org/gdcfkn DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90
Evans HE, de Lahunta A. Miller’s Anatomy of the Dog. 4th ed. St. Louis: Saunders. Can. Vet. J. 2012; 57(4):381. Available in: https://goo.su/yiOz0
Irvin J, Rajpurkar P, Ko M, Yu Y, Ciurea-Ilcus S, Chute C, Marklund H, Haghgoo B, Ball R, Shpanskaya K, Seekins J, Mong DA, Halabi SS, Sandberg JK, Jones R, Larson DB, Langlotz CP, Patel BN, Lungren MP, Ng AY. CheXpert: A large chest radiograph dataset with uncertainty labels and expert comparison. Proc. AAAI. Conf. Artif. Intell. 2019; 33(01):590–597. doi: https://doi.org/ghkh8x DOI: https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v33i01.3301590