Effect of systemic anticoagulants on fracture healing in rats tibia
Abstract
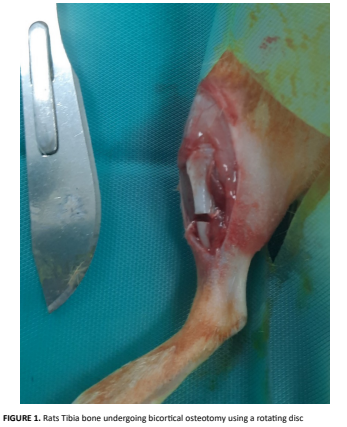
This study aimed to evaluate the effects of the systemic anticoagulants Apixaban, Rivaroxaban, Edoxaban, and Dabigatran on fracture healing. 48 female Spraque Dawley rats were divided into 6 groups with 8 rats in each group. Healthy Control group (n=8): no procedure was applied during the four-week experimental setup. Sham group (n=8): fractures were created in the right tibias of the subjects by surgical methods and the fractures were fixed with Kirshner wires in this group and all anticoagulant groups. No additional procedure was applied during the four (4) week to yhe sham group experimental setup. Throughout the 4-week experimental period, the animals were administered the following treatments via oral gavage three times per week: the Apixaban Group (n=8) received 5 mg/kg of apixaban; the Rivaroxaban Group (n=8) received 3 mg/kg of rivaroxaban; the Edoxaban Group (n=8) received 3 mg/kg of edoxaban; and the Dabigatran Group (n=8) received 10 mg/kg of dabigatran. At the end of the four-week experimental period, all rats were euthanized. Bone tissues were harvested, decalcified, and processed for histological analysis. A statistically significant difference was observed among the groups (P < 0.05). Post hoc analysis revealed that the Apixaban group (M = 55.75, SD= 3.41) and the Rivaroxaban group (M = 55.38, SD = 3.89) had significantly higher mean values compared to the Control group (M = 41.75, SD = 5.57) (P < 0.05). Additionally, the Dabigatran group (M = 44.00, SD = 4.66) and the Edoxaban group (M = 48.63, SD = 5.55) also differed significantly from the Control, with Edoxaban showing a statistically significant difference compared to Dabigatran (P < 0.05). No significant difference was observed between Apixaban and Rivaroxaban.The histopathological evaluations revealed that the administration of these anticoagulants had statistically significant effects on new bone formation compared to the control group.
Downloads
References
Brinker WO, Piermattei DL, Flo GL. Small Animal Orthopedics & Fracture Treatment. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Company; 1990.
Gartner LP, Hiatt JL. Color textbook of histology, 2nd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Company; 2001.
Vertenten G, Gasthuys F, Cornelissen M, Schacht E, Vlaminck L. Enhancing bone healing and regeneration: present and future perspectives in veterinary orthopaedics. Vet. Comp. Orthop. Traumatol. 2010; 23(3):153-162. doi: https://doi.org/bjthfb DOI: https://doi.org/10.3415/VCOT-09-03-0038
Schmidt-Bleek K, Petersen A, Dienelt A, Schwarz C, Duda GN. Initiation and early control of tissue regeneration - bone healing as a model system for tissue regeneration. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. [internet]. 2014; 14(2): 247-259. doi: https://doi.org/gsht8b DOI: https://doi.org/10.1517/14712598.2014.857653
Mafamane H, Hackenbroich C, Ellinghaus A, Schmidt- Bleek K. Research in Fracture Healing and Its Clinical Applications in the Veterinary Practice. J. Vet. Sci. Anim. Husb. [Internet]. 2017; 5(3):303. doi: https://doi.org/p8jh
Opal SM. Phylogenetic and functional relationships between coagulation and the innate immune response. Crit. Care Med. [Internet]. 2000; 28(9):S77-80. doi: https://doi.org/bzqhpx DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/00003246-200009001-00017
Schmidt-Bleek K, Schell H, Schulz N, Hoff P, Perka C, Buttgereit F, Volk HD, Lienau J, Duda GN. Inflammatory phase of bone healing initiates the regenerative healing cascade. Cell Tissue Res. [Internet]. 2012;347(3):567-573. doi: https://doi.org/dd3xbp DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-011-1205-7
Bozoglan A, Dundar S, Yildirim TT, Bulmus O, Ertugrul AS, Bozoglan MY, Tekin S, Toy VE. Effects of Different Levels of Restraint Stress on Bone-Implant Contact. J. Craniofacial Surg. [Internet]. 2019; 30(4):1294-1297. doi: https://doi.org/p8jk DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000005104
Weinz C, Schwarz T, Kubitza D, Mueck W, Lang D. Metabolism and excretion of rivaroxaban, an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor, in rats, dogs, and humans. Drug. Metab. Dispos. [Internet]. 2009; 37(5), 1056-1064. doi: https://doi.org/b3rgvm DOI: https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.108.025569
Wang L, He K, Maxwell B, Grossman SJ, Tremaine LM, Humphreys WG, Zhang D. Tissue distribution and elimination of [14C] apixaban in rats. Tissue distribution and elimination of [14C] apixaban in rats. Drug Metab. Dispos. [Internet]. 2011; 39(2), 256-264. doi: https://doi.org/bdjszz DOI: https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.110.036442
Jakowenko N, Nguyen S, Ruegger M, Dinh A, Salazar E, Donahue KR. Apixaban and rivaroxaban anti-Xa level utilization and associated bleeding events within an academic health system. Thromb. Res. [Internet]. 2020; 196:276-282. doi: https://doi.org/gpvt96 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2020.09.002
Wienen W, Stassen JM, Priepke H, Ries UJ, Hauel N. In-vitro profile and ex-vivo anticoagulant activity of the direct thrombin inhibitor dabigatran and its orally active prodrug, dabigatran etexilate. Thromb. haemost. [Internet]. 2007; 98(1):155-162. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1160/TH07-03-0183
Klebe D, Flores JJ, McBride DW, Krafft PR, Rolland WB, Lekic T, Zhang JH. Dabigatran ameliorates post-haemorrhagic hydrocephalus development after germinal matrix haemorrhage in neonatal rat pups. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2017; 37(9):3135-3149. doi: https://doi.org/p8jn DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X16684355
Bounameaux H, Camm AJ. Edoxaban: an update on the new oral direct factor Xa inhibitor. Drugs. [Internet]. 2014;74(11):1209-1231. Erratum in: Drugs. 2014;74(12):1455. doi: https://doi.org/f6pvdt DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-014-0261-1
Poulakos M, Walker JN, Baig U, David T. Edoxaban: A direct oral anticoagulant. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. [Internet]. 2017; 74(3):117-129. doi: https://doi.org/f9qbws DOI: https://doi.org/10.2146/ajhp150821
Prodinger PM, Burgkart R, Kreutzer K, Liska F, Pilge H, Schmitt A, Knödler M, Holzapfel BM, Hapfelmeier A, Tischer T, Bissinger O. Does Anticoagulant Medication Alter Fracture-Healing? A Morphological and Biomechanical Evaluation of the Possible Effects of Rivaroxaban and Enoxaparin Using a Rat Closed Fracture Model. PLoS One. [Internet]. 2016; 11(7):e0159669. doi: https://doi.org/p8jq DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0159669
Klüter T, Weuster M, Brüggemann S, Menzdorf L, Fitschen- Oestern S, Steubesand N, Acil Y, Pufe T, Varoga D, Seekamp A, Lippross S. Rivaroxaban does not impair fracture healing in a rat femur fracture model: an experimental study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. [Internet]. 2015; 16:79. doi: https://doi.org/f68bcv DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-015-0502-9
Namba S, Yamaoka-Tojo M, Kakizaki R, Nemoto T, Fujiyoshi K, Hashikata T, Kitasato L, Hashimoto T, Kameda R, Meguro K, Shimohama T, Tojo T, Ako J. Effects on bone metabolism markers and arterial stiffness by switching to rivaroxaban from warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. Heart Vessels. [Internet]. 2017; 32(8):977-982. doi: https://doi.org/p8jr DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00380-017-0950-2
Lau WC, Chan EW, Cheung CL, Sing CW, Man KKC, Lip GYH, Siu CW, Lam JKY, Lee ACH, Wong ICK. Association between dabigatran vs warfarin and risk of osteoporotic fractures among patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. JAMA. [Internet]. 2017; 317(11):1151–1158. doi: https://doi.org/f9vkw4 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2017.1363
Norby FL, Bengtson LGS, Lutsey PL, Chen LY, MacLehose RF, Chamberlain AM, Rapson I, Alonso A. Comparative effectiveness of rivaroxaban versus warfarin or dabigatran for the treatment of patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. [Internet]. 2017; 17(1):238. doi: https://doi.org/gbxb73 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-017-0672-5
Kyriakaki I, Karanikola T, Lillis T, Kontonasaki E, Dabarakis N. Effect of direct oral anticoagulant dabigatran on early bone healing: An experimental study in rats. J. Adv. Periodontol. Implant Dent. [Internet]. 2023; 15(2):86-92. doi: https://doi.org/p8jt DOI: https://doi.org/10.34172/japid.2023.020
Butler AJ, Eismont FJ. Effects of Anticoagulant Medication on Bone-Healing. JBJS Reviews. [Internet]. 9(5):e20.00194. doi: https://doi.org/p8jv DOI: https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.RVW.20.00194
Gómez-Outes A, Terleira-Fernández AI, Suárez-Gea ML, Vargas-Castrillón E. Dabigatran, rivaroxaban, or apixaban versus enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis after total hip or knee replacement: systematic review, meta-analysis, and indirect treatment comparisons. BMJ. [Internet]. 2012; 344:e3675. doi: https://doi.org/gb3r9b DOI: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.e3675
Fusaro M, Dalle Carbonare L, Dusso A, Arcidiacono MV, Valenti MT, Aghi A, Pasho S, Gallieni M. Differential Effects of Dabigatran and Warfarin on Bone Volume and Structure in Rats with Normal Renal Function. PLoS One. [Internet]. 2015; 10(8):e0133847. doi: https://doi.org/f7z2xz DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0133847