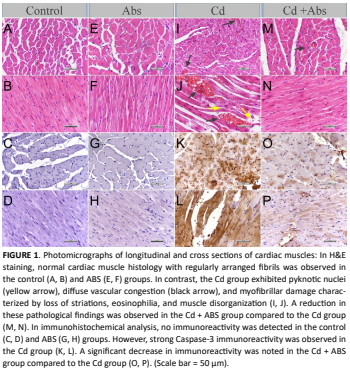
Effect of Ankaferd blood stopper on Cadmium-induced heart damage in male rats
Abstract
Cadmium (Cd), a widespread environmental contaminant, is known to cause tissue injury through mechanisms involving oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. The heart is particularly vulnerable to such toxic effects. Ankaferd Blood Stopper, a standardized herbal hemostatic agent, also exhibits notable antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic activities. This study aimed to explore the potential protective effects of Ankaferd Blood Stopper against cadmium-induced cardiac injury, evaluating whether Ankaferd Blood Stopper administration mitigates histopathological and apoptotic damage in cardiac tissue caused by cadmium toxicity in rats. Thirtytwo male Wistar Albino rats (350–450 g) were divided into four groups (n=8 each): Control (saline, i.p.), Cd (2.5 mg/ kg CdCl₂, i.p.), Ankaferd Blood Stopper (0.5 mL ABS, i.p.), and Cd + Ankaferd Blood Stopper (CdCl₂ + Ankaferd Blood Stopper, both i.p.). After treatment, cardiac tissues were collected and evaluated using histopathological staining and Caspase-3 immunohistochemistry. Blood samples were also collected for biochemical analysis. Cadmium exposure resulted in marked myocardial damage, including inflammatory infiltration, vascular congestion, and disorganized myofibers. Caspase-3 expression confirmed increased apoptotic activity. Ankaferd Blood Stopper administration significantly reduced histopathological lesions and Caspase-3 immunoreactivity in the Cd + Ankaferd Blood Stopper group, suggesting a protective effect. Ankaferd Blood Stopper effectively attenuated cadmium- induced cardiac injury, likely due to its antioxidant and anti- inflammatory properties. These findings indicate that Ankaferd Blood Stopper may offer therapeutic benefits in preventing or alleviating heavy metal-induced cardiovascular damage. Additional research is needed to validate these effects in long- term and clinical models.
Downloads
References
Gunes E. Antioxidant effects of Ankaferd Blood Stopper- doped polyvinyl pyrrolidone in an experimental model created in insects. Food Chem. Toxicol. [Internet]. 2021; 148:111935. doi: https://doi.org/p9hv DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2020.111935
Ilhan I, Buyukbayram HI. Protective role of Ankaferd Blood Stopper on cadmium-induced acute nephrotoxicity. Med. J. SDU. [Internet]. 2023; 30(1):111-118. doi: https://doi.org/p9hw DOI: https://doi.org/10.17343/sdutfd.1239914
Ugur A, Sarac N, Cankal DA, Ozle M. The antioxidant and antimutagenic activities of Ankaferd Blood Stopper, a natural hemostatic agent used in dentistry. Turk. J. Med. Sci. [Internet]. 2016; 46(3):657-663. doi: https://doi.org/g9kbvr DOI: https://doi.org/10.3906/sag-1504-62
Arici E, Polat M. Determination of major heavy metal levels in pepper gas used as chemical agents in CBRN field. SDU J. Health Sci. [Internet]. 2024; 15(2):226-235. doi: https://doi.org/p9hz DOI: https://doi.org/10.22312/sdusbed.1480468
Ozbolat G, Tuli A. Effects of heavy metal toxicity on human health. Arch. Med. Rev. J. [Internet]. 2016; 25(4):502-521. doi: https://doi.org/p9h2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.17827/aktd.253562
Polat M, Ogut S. Heavy metals in some medicinal plants sold in herbal shops. Fresenius Environ. Bull. [Internet]. 2018 [cited 19 Jul 2025]; 27(4):1999-2002. Available in: https://goo.su/51tlgC
Jarup L. Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br. Med. Bull. [Internet]. 2003; 68(1):167-182. doi: https://doi.org/cqwm49 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/bmb/ldg032
Gökdemir GS, Çakmak S, Demirtaş B, Gökdemir MT, Sogut O, Canpolat–Erkan RE, Aşır F, Yokus B. El efecto de la intoxicación aguda por monóxido de carbono en la necrosis cardíaca en ratas: en relación con los niveles de adiponectina. Rev. Cient. FCV-LUZ. [Internet]. 2025; 35(1):8. doi: https://doi.org/p9h4 DOI: https://doi.org/10.52973/rcfcv-e35532
Bridges CC, Zalups RK. Molecular and ionic mimicry and the transport of toxic metals. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. [Internet]. 2005; 204(3):274-308. doi: https://doi.org/cpg8kx DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2004.09.007
Joseph P. Mechanisms of cadmium carcinogenesis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. [Internet]. 2009; 238(3):272-279. doi: https://doi.org/cwd3gk DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2009.01.011
Aktop S, EmekliAlturfan E, Ozer C, Gonul O, Garip H, Yarat A, Goker K. Effects of Ankaferd Blood Stopper and Celox on the tissue factor activities of warfarin-treated rats. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. [Internet]. 2013; 20(1):1621. doi: https://doi.org/f5kmzh DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1076029613490254
Bell RR, Nonavinakere VK, Soliman MR. Intratracheal exposure of the guinea pig lung to cadmium and/ or selenium: a histological evaluation. Toxicol. Lett. [Internet]. 2000; 114(1-3):101-109. doi: https://doi.org/b2cq2n DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4274(99)00286-6
Gulle K, Ceri NG, Akpolat M, Arasli M, Demirci B. The effects of dexpanthenol in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: histological, histochemical and immunological evidences. Histol. Histopathol. [Internet]. 2014 [cited 14 Jul 2025]; 29(10):1305-1313. Available in: https://goo.su/IenUcR
Skalli O, Gabbiani G. The biology of the myofibroblast relationship to wound contraction and fibrocontractive disease. In: Clark RAF, Henson PM, editors. The Molecular and Cellular Biology of Wound Repair. New York: Plenum Press; 1988. p. 373-402. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-1795-5_17
Nohl H. Generation of superoxide radicals as byproducts of cellular respiration. Ann. Biol. Clin. (Paris). 1994; 52(3):199-204.
Senel O, Cetinkale O, Ozbay G, Ahcioglu F, Bulan R. Oxygen free radicals impair wound healing in ischemic rat skin. Ann. Plast. Surg. [Internet]. 1997; 39(5):516-523. doi: https://doi.org/b62xjd DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/00000637-199711000-00012
Agaev AIu, Nikolaev AV, Abasov BKh, Mamedov LA, Zakharov VV, Bashirov EA, Bagirov GS. Antioxidant therapy of purulent wounds in animal experiments. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 1989; 108(7):35-37. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00839774
Bergamini CM, Gambetti S, Dondi A, Cervellati C. Oxygen, reactive oxygen species, and tissue damage. Curr. Pharm. Des. [Internet]. 2004; 10(14):1611-1626. doi: https://doi.org/fctrhh DOI: https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612043384664
Salvi A, Battaglia V, Brunati AM,La Rocca N, Tibaldi E, Pietrangeli P, Marcocci L, Mondovì B, Rossi CA, Toninello A. Catalase takes part in rat liver mitochondria oxidative stress defense. J. Biol. Chem. [Internet]. 2007; 282(33):24407-24415. doi: https://doi.org/cfmtms DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M701589200
Attia AA, El-Mazoudy RH, El-Shenawy NS. Antioxidant role of propolis extract against oxidative damage of testicular tissue induced by insecticide chlorpyrifos in rats. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. [Internet]. 2012; 103(2):87-93. doi: https://doi.org/mh2g DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2012.04.002
Ozen T, Korkmaz H. Modulatory effect of Urtica dioica L. (Urticaceae) leaf extract on biotransformation enzyme systems, antioxidant enzymes, lactate dehydrogenase and lipid peroxidation in mice. Phytomedicine. [Internet]. 2003; 10(5):405-415. doi: https://doi.org/dzszb9 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1078/0944-7113-00275
Rezg R, Mornagui B, Kamoun A, El-Fazaa S, Gharbi N. Effect of subchronic exposure to malathion on metabolic parameters in the rat. C. R. Biol. [Internet]. 2007; 330(2):143-147. doi: https://doi.org/cpp239 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crvi.2006.11.002
Romeu M, Mulero M, Giralt M, Folch J, Nogués MR, Torres A, Fortuño A, Sureda FX, Cabré M, Paternáin JL, Mallol J. Parameters related to oxygen free radicals in erythrocytes, plasma, and epidermis of the hairless rat. Life Sci. [Internet]. 2002; 71(15):1739-1749. doi: https://doi.org/fwhd5s DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0024-3205(02)01946-X
Tuthill DD, Bayer V, Gallagher AM, Drohan WN, MacPhee MJ. Assessment of topical hemostats in a renal hemorrhage model in heparinized rats. J. Surg. Res. [Internet]. 2001; 95(2):126-132. https://doi.org/d7c5j7 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jsre.2000.6027
Elg M, Gustafsson D, Carlsson S. Antithrombotic effects and bleeding time of thrombin inhibitors and warfarin in the rat. Thromb. Res. [Internet]. 1999; 94(3):187-197. doi: https://doi.org/d86rkp DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0049-3848(98)00213-8
Merian E. Metals and their compounds in the environment: Occurrence, analysis, and biological relevance. Weinheim: VCH; 1991.
Appleton J, Lee KM, Sawicka-Kapusta K, Damek M, Cooke M. Heavy metal content in the teeth of bank vole (Clethrionomys glareolus) as an exposure marker of environmental pollution in Poland. Environ. Pollut. [Internet]. 2000; 110(3):441-449. doi: https://doi.org/cksr8d DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(99)00318-8
Kjellstrom T, Elinder CG, Friberg L. Conceptual problems in establishing the critical concentration of cadmium in human kidney cortex. Environ. Res. [Internet]. 1984; 33(2):284-295. doi: https://doi.org/cgbhnb DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-9351(84)90025-2
Sangartit W, Kukongviriyapan U, Donpunha W, Pakdeechote P, Kukongviriyapan V, Surawattanawan P, Greenwald SE. Tetrahydrocurcumin protects against cadmium-induced hypertension, raised arterial stiffness and vascular remodeling in mice. PLoS One. [Internet]. 2014; 9(12):e114908. doi: https://doi.org/f6xb8d DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0114908
Saleh RM, Awadin WF. Biochemical and histopathological changes of subacute cadmium intoxication in male rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. [Internet]. 2017; 24(32):25475- 25481. doi: https://doi.org/gckjns DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0348-9
Bhattacharjee B,PalP K, Ghosh A K,Mishra S, Chattopadhyay A, Bandyopadhyay D. Aqueous bark extract of Terminalia arjuna protects against cadmiuminduced hepatic and cardiac injuries in male Wistar rats through antioxidative mechanisms. Food Chem. Toxicol. [Internet]. 2019; 124:249264. doi: https://doi.org/gqxjrm DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2018.12.008
Li Y, Li H, Xiao L, Zhou L, Shentu J, Zhang X, Fan J. Hemostatic efficiency and wound healing of natural zeolite granules in lethal rabbit model of complex groin injury. Materials. [Internet]. 2012; 5(12):2586-2595. doi: https://doi.org/f4h5zj DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ma5122586
Tucovic D, Popov-Aleksandrov A, Mirkov I, Ninkov M, Kulas J, Zolotarevski L, Vukojevic V, Mutic J, Tatalovic N, Kataranovski M. Oral cadmium exposure affects skin immune reactivity in rats. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. [Internet]. 2018; 164:12-20. doi: https://doi.org/gfn3vc DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.07.117
Halliwell B, Hoult JR, Blake DR. Oxidants, inflammation, and anti-inflammatory drugs. FASEB J. [Internet]. 1988; 2(13):2867-2873. doi: https://doi.org/p9jg DOI: https://doi.org/10.1096/fasebj.2.13.2844616
Cheel J, Van Antwerpen P, Tůmová L, Onofre G, Vokurková D, ZouaouiBoudjeltia K, Vanhaeverbeek M, Nève J. Free radical-scavenging, Antioxidant and immunostimulating effects of licorice infusion (Glycyrrhiza glabra L.). Food Chem. [Internet]. 2010; 122(3):508-517. doi: https://doi.org/cvcgx8 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.02.060
Hong YK, Wu HT, Ma T, Liu WJ, He XJ. Effects of Glycyrrhiza glabra polysaccharides on immune and antioxidant activities in high-fat mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. [Internet]. 2009; 45(1):61-64. doi: https://doi.org/c67665 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2009.04.001